年终惯例是做年度总结,而恰好每年年初都会给自己定一个读书目标。以前总是达标之后心情愉悦便没有然后了,今年突发奇想,想看看过去的一年里,自己都读了什么书,以便有的放矢地安排下一年的读书目标。
需求有了,接下来则是要获取数据了。凑巧我有个习惯,每看一本书会在豆瓣上标记一下。因此,我在豆瓣上的已读清单就是最好的原数据。
创建爬虫
对于爬虫工具的选择,以方便为主,所以我选了scrapy。
安装好 scrapy 后,创建一个名为 book 的项目: 1
| scrapy startproject book
|
登陆豆瓣后,找到页面“我读过的书”,就可以看到已阅图书列表了。该页面的 URL 有以下模式: 1
| https://book.douban.com/people/{豆瓣id}/collect
|
经过确认,这个页面确实是公开的,这样,我们就不需要进行模拟登陆了。(虽然省去了这一步,但是不知道豆瓣的产品经理是如何考量的,为什么要把用户这个比较私密的属性赤裸裸地暴露在阳光虾呢?)
接下来,借助 chrome 的开发者工具,观察下每一个图书项的组成部分: 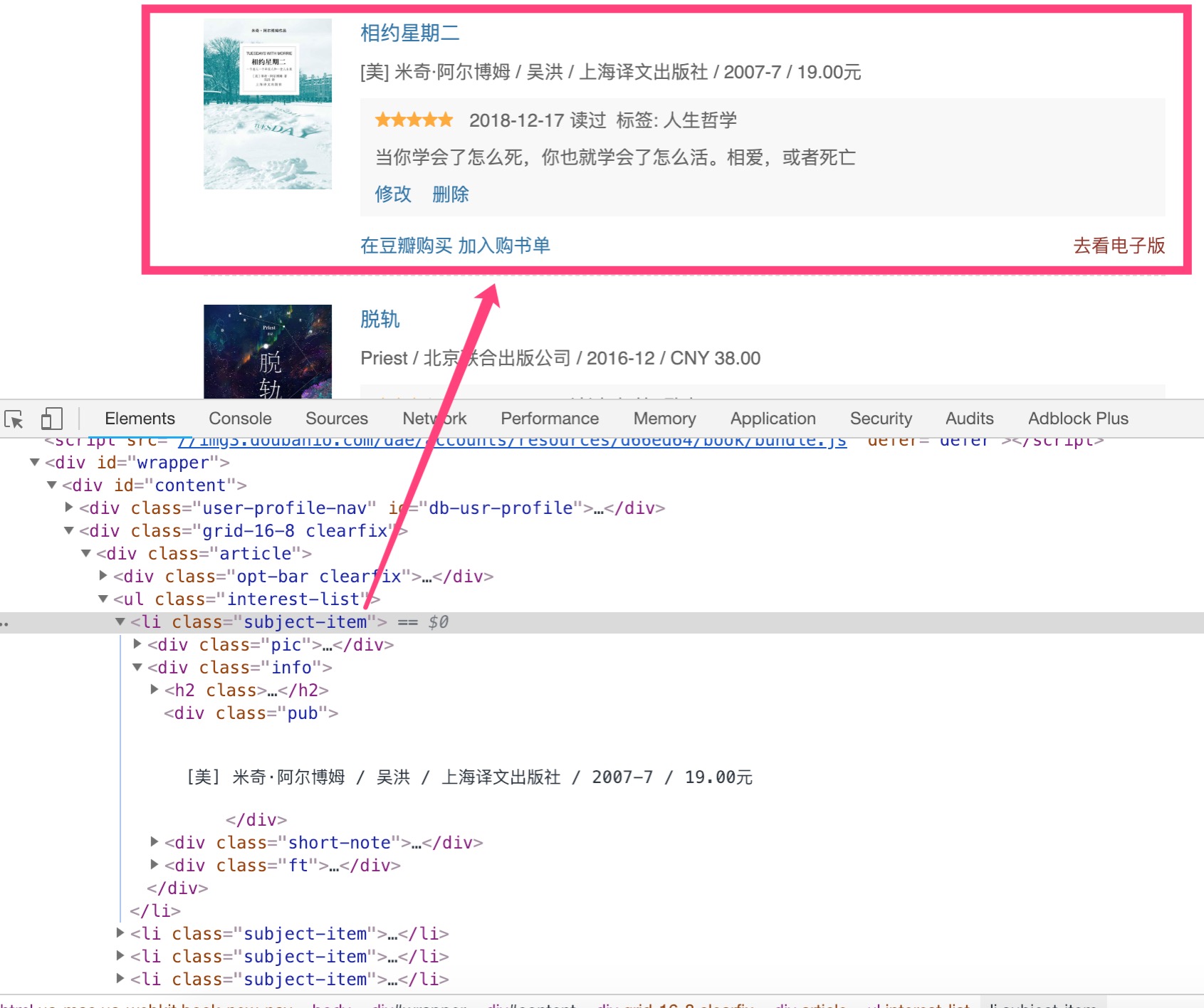
可以发现几点(以下用 xpath 表示法): * 每一个图书项://li[@class="subject-item" * 图书名称:div[@class="info"]/h2/a/@title * 图书详情页 url:div[@class="info"]/h2/a/@href * 出版信息:div[@class="info"]/div[@class="pub"]/text() * 评价信息:div[@class="info"]/div[@class="short-note"]/div[1]/span[1]/@class * 读完的日期:div[@class="info"]/div[@class="short-note"]/div[1]/span[@class="date"]/text() * 标签信息:div[@class="info"]/div[@class="short-note"]/div[1]/span[@class="tags"]/text() * 评价信息:div[@class="info"]/div[@class="short-note"]/p[@class="comment"]/text() * 以及下一页://span[@class="next"]/a/@href
因此,我们可以在 book/items.py 中定义我们所需要的属性:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| class BookItem(scrapy.Item):
name = scrapy.Field()
url = scrapy.Field()
pub = scrapy.Field()
rating = scrapy.Field()
readDate = scrapy.Field()
tags = scrapy.Field()
comment = scrapy.Field()
|
然后在 book/spiders 目录下创建一个爬虫文件 collect_spider.py。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| class CollectSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "collect"
allowed_domains = ["douban.com"]
start_urls = [
"https://book.douban.com/people/******/collect"
]
def parse(self, response):
for subItem in response.xpath('//li[@class="subject-item"]'):
item = BookItem()
item['name'] = "".join(subItem.xpath('div[@class="info"]/h2/a/@title').extract()).strip()
item['url'] = subItem.xpath('div[@class="info"]/h2/a/@href').extract_first(default="Missing")
item['pub'] = "".join(subItem.xpath('div[@class="info"]/div[@class="pub"]/text()').extract()).strip()
item['rating'] = subItem.xpath('div[@class="info"]/div[@class="short-note"]/div[1]/span[1]/@class').extract_first(default="Missing").strip()
item['readDate'] = subItem.xpath('div[@class="info"]/div[@class="short-note"]/div[1]/span[@class="date"]/text()').extract_first(default="Missing")
item['tags'] = "".join(subItem.xpath('div[@class="info"]/div[@class="short-note"]/div[1]/span[@class="tags"]/text()').extract())
item['comment'] = "".join(subItem.xpath('div[@class="info"]/div[@class="short-note"]/p[@class="comment"]/text()').extract()).strip()
yield item
next_page = response.xpath('//span[@class="next"]/a/@href')
if next_page:
url = response.urljoin(next_page[0].extract())
print("next: ", url)
yield scrapy.Request(url, callback=self.parse)
|
之后可以运行下看看爬取结果: 1
| $ scrapy crawl collect -o items.json
|
book/settings.py 中的 USER_AGENT 为配置项 USER_AGENT = 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/55.0.2883.87 Safari/537.36'
获取书籍更多的出版信息
为了获得更多的出版信息(如 ISBN),我们需要爬取每个图书的详情页。详情页的 url 我们在上一个步骤就已经可以获得了。
在 book/items.py 中添加详情定义:
1
2
3
4
| class BookItem(scrapy.Item):
....
isbn = scrapy.Field()
morePub = scrapy.Field()
|
分析页面代码后修改 collect_spider.py:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| def parse(self, response):
for subItem in response.xpath('//li[@class="subject-item"]'):
....
if item['url'] and item['url'] != 'Missing':
request = scrapy.Request(item['url'], callback=self.parse_item)
request.meta['item'] = item
yield request
else:
yield item
next_page = response.xpath('//span[@class="next"]/a/@href')
if next_page:
url = response.urljoin(next_page[0].extract())
print("next: ", url)
yield scrapy.Request(url, callback=self.parse)
def parse_item(self, response):
item = response.meta['item']
item['morePub'] = response.xpath('//*[@id="info"]/text()').extract()
if len(item['morePub']) >= 2:
isbn = item["morePub"][-2].strip()
if isbn:
item['isbn'] = isbn
yield item
|
确定书籍所属类别
因为想对图书类别进行分析,而豆瓣图书是没有类别信息的,所以得想个办法获取到对应图书的类别信息。
通过 CALIS 联合目录公共检索系统 就可以根据 ISBN 查询到对应到图书类别信息。
接下来就是分析模拟查询请求了。再次借助 chrome 的开发者工具,进行一次图书检索,看看会出现什么样子的请求交互:
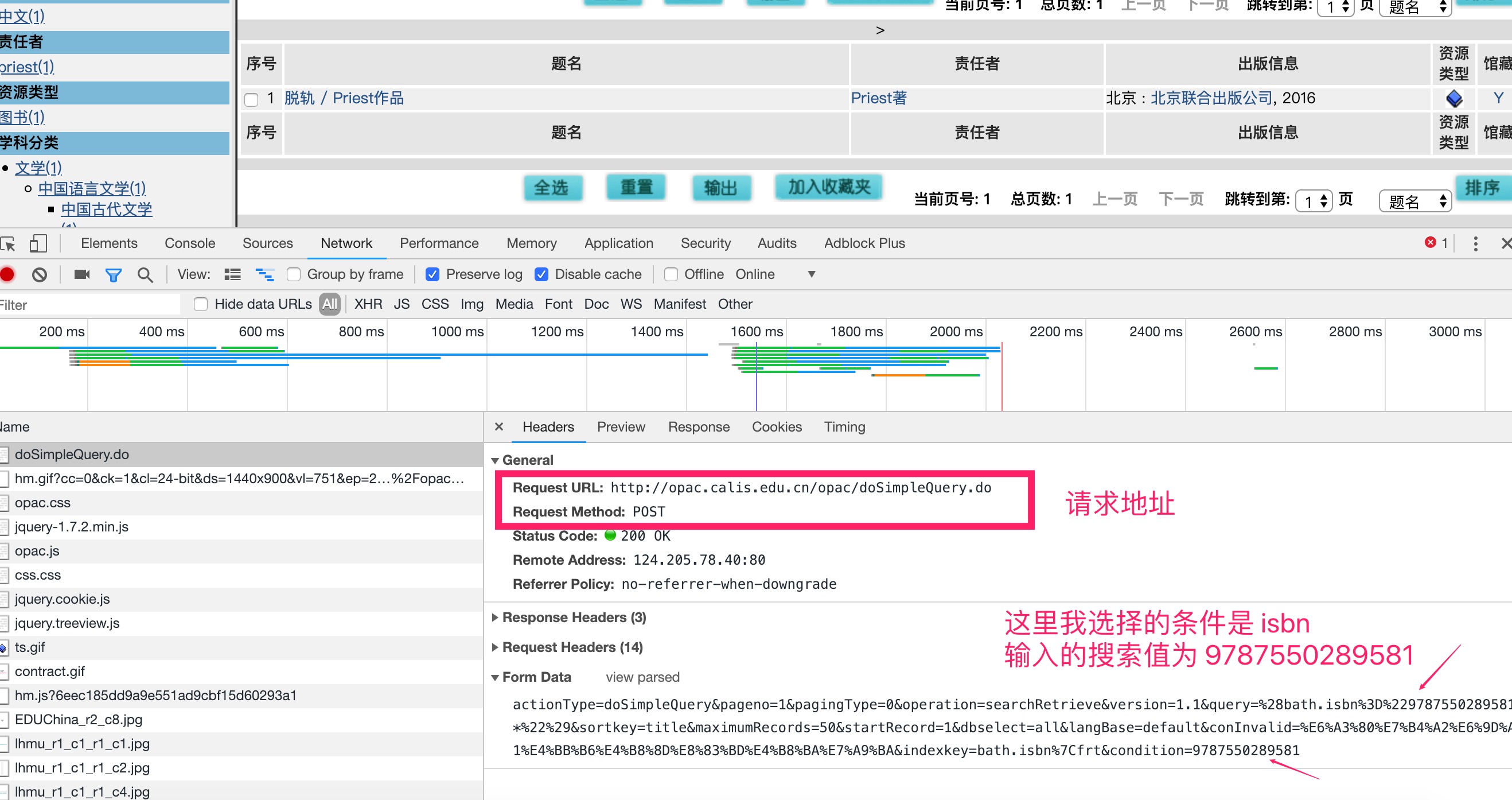
因此,查询方法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| def queryCatagory(isbn):
url = "http://opac.calis.edu.cn/opac/doSimpleQuery.do"
data = {
"actionType": "doSimpleQuery",
"pageno": 1,
"pagingType": 0,
"operation": "searchRetrieve",
"version": 1.1,
"query": '(bath.isbn="{0}*")'.format(isbn),
"sortkey": "title",
"maximumRecords": 50,
"startRecord": 1,
"dbselect": "all",
"langBase": "default",
"conInvalid": "检索条件不能为空",
"indexkey": "bath.isbn|frt",
"condition": isbn,
}
resp = requests.post(url, data)
if resp.status_code != 200: return "not found"
page = etree.HTML(resp.text)
info = page.xpath('//*[@id="browser"]/li/span/a/u')
if info:
return info[0].text
return "not found"
|
先将类别信息添加到 book/items.py 中:
1
2
3
| class BookItem(scrapy.Item):
....
catagory = scrapy.Field()
|
我们把上面的方法添加在 collect_spider.py 中,然后在获取到 isbn 后查询类别信息:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| def parse_item(self, response):
....
if len(item['morePub']) >= 2:
....
if isbn:
....
item['catagory'] = queryCatagory(isbn)
yield item
|
最后运行下爬虫即可:
1
| $ scrapy crawl collect -o items.json
|
小结一下
数据分析的第一步大抵都是确定分析目标,然后根据目标获取相应数据。
接下来,就是撸起袖子开始分析了~



